Unlocking the Potential of Multilayer Boards: Applications and Benefits
2024-05-24
In the world of electronics, the term "multilayer board" often conjures up images of sophisticated circuitry and intricate design. But what exactly is a multilayer board, and why are they so important in today's technology landscape? Let's delve into the world of multilayer boards, understand their construction, and explore their diverse applications.
What is a Multilayer Board?
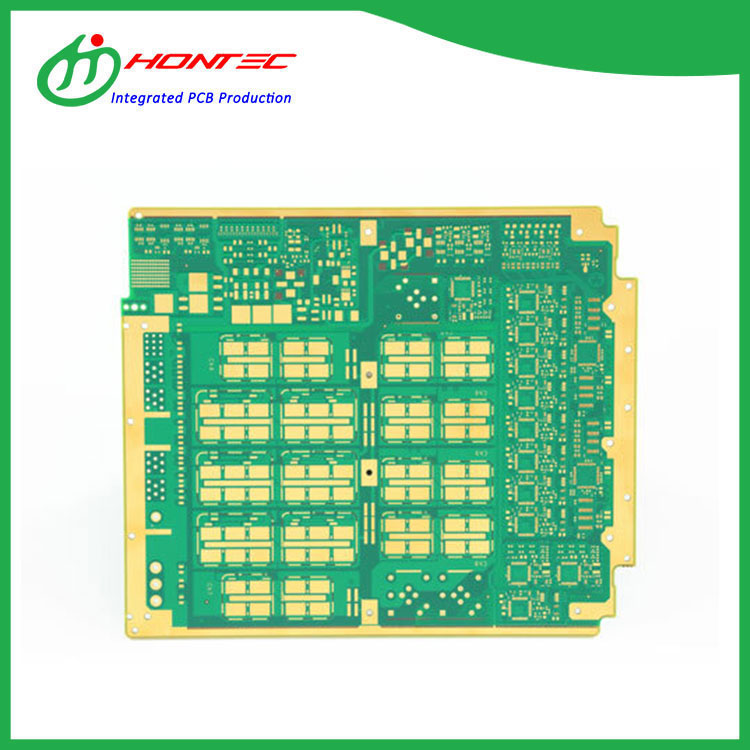
A multilayer board, also known as a multilayer printed circuit board (PCB), is an electronic component that consists of multiple layers of conductive material, usually copper, sandwiched between layers of non-conductive material, typically a dielectric substrate. These layers are bonded together through a process called lamination, resulting in a highly complex yet compact structure that can accommodate a high density of circuitry.
The key components of a multilayer board include:
Conductive layers: These are the layers that carry the electrical signals. They are typically made of copper and etched to form the desired circuitry.
Dielectric layers: These non-conductive layers separate the conductive layers, providing electrical isolation and support.
Vias: Small holes that connect the conductive layers, allowing signals to travel vertically between layers.
Main Applications of Multilayer Boards
Multilayer boards are widely used in a variety of electronic applications due to their ability to handle complex circuitry in a compact form factor. Here are some of the main applications of multilayer boards:
Computer Hardware: Computers and servers rely on multilayer boards to connect their various components, such as processors, memory, and storage devices. The high density of circuitry and small size of multilayer boards are crucial for ensuring efficient data transfer and minimizing power consumption.
Communication Equipment: Telecommunication devices like routers, switches, and base stations utilize multilayer boards to handle high-speed data transmission. The ability to route signals efficiently between layers makes multilayer boards an ideal choice for these applications.
Consumer Electronics: From smartphones and tablets to TVs and game consoles, consumer electronics rely on multilayer boards to power their advanced features and functionalities. The compact size and reliability of multilayer boards make them a perfect fit for these devices.
Medical Equipment: Medical devices, such as MRI machines, X-ray scanners, and patient monitoring systems, require high-precision circuitry to ensure accurate readings and reliable operation. Multilayer boards provide the necessary stability and precision for these critical applications.
Industrial Automation: In factories and production lines, multilayer boards are used to control and monitor various machines and processes. Their ability to handle complex circuitry and withstand harsh environments makes them essential for ensuring smooth operation and maximum efficiency.
Conclusion
Multilayer boards are an essential component of modern electronics, enabling the development of sophisticated devices with high-density circuitry and compact form factors. From computers and communication equipment to consumer electronics and medical devices, multilayer boards are playing an increasingly important role in powering our digital world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of multilayer boards in the future.